Mini guía parte 3

Mini Guía Parte 3: Conjugación de Verbos en Español
Introducción
En esta guía, nos enfocamos en tres tiempos verbales esenciales del modo indicativo: Presente, Pretérito Indefinido y Futuro Simple. Estos tiempos son cruciales para mantener conversaciones básicas y efectivas en español. Aprender a conjugarlos te permitirá expresarte claramente en diferentes contextos.
Conjugación
Conjugación Regular
Presente del Indicativo
Para conjugar los verbos regulares en el presente, se elimina la terminación del infinitivo (-ar, -er, -ir) y se agregan las terminaciones correspondientes al sujeto.
-AR
| Pronombre | Terminación -AR |
|---|---|
| yo | -o |
| tú | -as |
| él/ella/usted | -a |
| nosotros/as | -amos |
| vosotros/as | -áis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | -an |
-ER
| Pronombre | Terminación -ER |
|---|---|
| yo | -o |
| tú | -es |
| él/ella/usted | -e |
| nosotros/as | -emos |
| vosotros/as | -éis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | -en |
-IR
| Pronombre | Terminación -IR |
|---|---|
| yo | -o |
| tú | -es |
| él/ella/usted | -e |
| nosotros/as | -imos |
| vosotros/as | -ís |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | -en |
Ejemplos de Verbos Regulares en Presente
- Hablar: yo hablo, tú hablas, él/ella habla (to speak: I speak, you speak, he/she speaks)
- Comer: yo como, tú comes, él/ella come (to eat: I eat, you eat, he/she eats)
- Vivir: yo vivo, tú vives, él/ella vive (to live: I live, you live, he/she lives)
Pretérito Indefinido
El pretérito indefinido se utiliza para hablar de acciones completadas en el pasado.
-AR
| Pronombre | Terminación -AR |
|---|---|
| yo | -é |
| tú | -aste |
| él/ella/usted | -ó |
| nosotros/as | -amos |
| vosotros/as | -asteis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | -aron |
-ER/-IR
| Pronombre | Terminación -ER/-IR |
|---|---|
| yo | -í |
| tú | -iste |
| él/ella/usted | -ió |
| nosotros/as | -imos |
| vosotros/as | -isteis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | -ieron |
Ejemplos de Verbos Regulares en Pretérito Indefinido
- Hablar: yo hablé, tú hablaste, él/ella habló (to speak: I spoke, you spoke, he/she spoke)
- Comer: yo comí, tú comiste, él/ella comió (to eat: I ate, you ate, he/she ate)
- Vivir: yo viví, tú viviste, él/ella vivió (to live: I lived, you lived, he/she lived)
Futuro Simple
Para formar el futuro simple, se agrega la terminación correcta al infinitivo del verbo.
-AR/-ER/-IR
| Pronombre | Terminación -AR/-ER/-IR |
|---|---|
| yo | -é |
| tú | -ás |
| él/ella/usted | -á |
| nosotros/as | -emos |
| vosotros/as | -éis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | -án |
Ejemplos de Verbos Regulares en Futuro Simple
- Hablar: yo hablaré, tú hablarás, él/ella hablará (to speak: I will speak, you will speak, he/she will speak)
- Comer: yo comeré, tú comerás, él/ella comerá (to eat: I will eat, you will eat, he/she will eat)
- Vivir: yo viviré, tú vivirás, él/ella vivirá (to live: I will live, you will live, he/she will live)
Conjugación Irregular
Algunos verbos tienen conjugaciones irregulares en estos tiempos. Aquí hay una lista de verbos irregulares y sus conjugaciones:
Presente
| Verbo | Conjugación |
|---|---|
| Ser | soy, eres, es, somos, sois, son (to be: I am, you are, he/she is, we are, you all are, they are) |
| Ir | voy, vas, va, vamos, vais, van (to go: I go, you go, he/she goes, we go, you all go, they go) |
| Tener | tengo, tienes, tiene, tenemos, tenéis, tienen (to have: I have, you have, he/she has, we have, you all have, they have) |
Pretérito Indefinido
| Verbo | Conjugación |
|---|---|
| Ser/Ir | fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, fueron (to be/to go: I was/went, you were/went, he/she was/went, we were/went, you all were/went, they were/went) |
| Tener | tuve, tuviste, tuvo, tuvimos, tuvisteis, tuvieron (to have: I had, you had, he/she had, we had, you all had, they had) |
| Estar | estuve, estuviste, estuvo, estuvimos, estuvisteis, estuvieron (to be: I was, you were, he/she was, we were, you all were, they were) |
Futuro Simple
| Verbo | Conjugación |
|---|---|
| Decir | diré, dirás, dirá, diremos, diréis, dirán (to say: I will say, you will say, he/she will say, we will say, you all will say, they will say) |
| Hacer | haré, harás, hará, haremos, haréis, harán (to do/make: I will do/make, you will do/make, he/she will do/make, we will do/make, you all will do/make, they will do/make) |
| Poder | podré, podrás, podrá, podremos, podréis, podrán (to be able to: I will be able to, you will be able to, he/she will be able to, we will be able to, you all will be able to, they will be able to) |
Usos
Presente
- Acciones habituales: Yo hablo español todos los días. (I speak Spanish every day.)
- Acciones en progreso: Ahora mismo, yo estudio para mi examen. (Right now, I am studying for my exam.)
Pretérito Indefinido
- Acciones completadas en el pasado: Ayer, comí pizza. (Yesterday, I ate pizza.)
- Acciones puntuales: El año pasado, viajé a España. (Last year, I traveled to Spain.)
Futuro Simple
- Acciones futuras: Mañana, iré al cine. (Tomorrow, I will go to the cinema.)
- Predicciones: Habrá lluvia esta tarde. (There will be rain this afternoon.)
Marcadores Temporales
Presente
- Siempre (always): Siempre como a las dos. (I always eat at two.)
- Ahora (now): Ahora estudio español. (Now I study Spanish.)
Pretérito Indefinido
- Ayer (yesterday): Ayer fui al mercado. (Yesterday I went to the market.)
- El año pasado (last year): El año pasado viajé a México. (Last year I traveled to Mexico.)
Futuro Simple
- Mañana (tomorrow): Mañana veré a mis amigos. (Tomorrow I will see my friends.)
- La próxima semana (next week): La próxima semana tendré una reunión. (Next week I will have a meeting.)
Tips y Recordatorios
- Recordatorio: En el presente, algunos verbos son irregulares y no siguen las reglas estándar.
- Tip: Usa el contexto de la conversación para determinar el tiempo
En esta parte de la guía nos enfocaremos solo en la parte de los verbos, enseñaremos solo tres formas de conjugación del indicativo; El presente, el pretérito indefinido y el futuro simple, esta parte esta enfocada para que podamos hablar y tener conversaciones básicas en cualquiera de estos tiempo.
Para poder entender y conjugar los verbos es muy importante entender su estructura y sus morfemas (Un morfema es la parte más pequeña que tiene sentido en una palabra), algunas personas la conocen como “raíz” y “parte flexiva”.
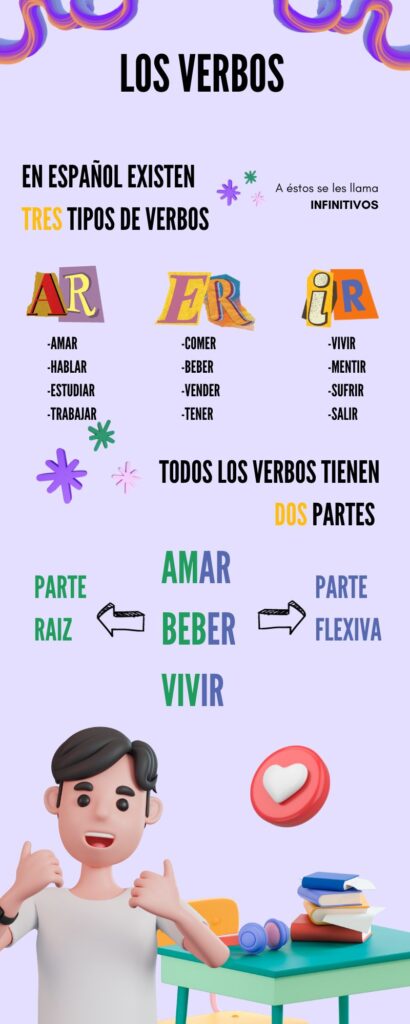
Los tiempos se forman añadiendo varias terminaciones para cada persona a la raíz del verbo después de eliminar la parte flexiva y para la mayoría de ellos siguen patrones regulares

En las siguientes tablas presentamos, presente, pretérito indefinido, y futuro simple como opciones básicas, pero recuerda que hay más tiempos verbales.
El presente del indicativo en español
El presente en español se escribe, eliminando la parte flexiva y añadiendo sus respectivas terminaciones, dependiendo del sujeto.
´I verb´
| Sujeto | HABLAR | BEBER | VIVIR |
| Yo | hablo | bebo | vivo |
| Tú | hablas | bebes | vives |
| Él, Ella, Elle, Usted | habla | bebe | vive |
| Nosotros, Nosotras, Nosotres | hablamos | bebemos | vivimos |
| Ellos, Ellas, Elles, Ustedes | hablan | bebemos | viven |
Pretérito indefinido
En español existen varias formas para hablar de pasado, estos tiempos se les conocen como, pretéritos pero aquí te enseñaremos el pretérito indefinido, o también se le conoce como, pretérito perfecto simple.
I [verbed]”
Sujeto | HABLAR | BEBER | VIVIR |
| Yo | hablé | bebí | viví |
| Tú | hablaste | bebiste | viviste |
| Él, Ella, Elle, Ustedes | habló | bebió | vivió |
| Nosotros, Nosotras, Nosotres | hablamos | bebimos | vivimos |
| Ellos, Ellas, Elles, Ustedes | hablaron | bebieron | vivieron |
Futuro simple
La forma en que se conjuga el futuro es un poco diferente a los dos ultimos tiempos. Para conjugar los verbos en futuro simple no es necesario remover la parte flexiva del verbo, tomamos todo el verbo y solo agregaremos la parte flexica que le corresponda.
I will [verb]”

NOTA: En el futuro las tres categorías de los verbos tienen las mismas terminaciones, en este caso las terminaciones se agregan al infinitivo.
“I will [verb]”
Sujeto | HABLAR | BEBER | VIVIR |
| Yo | hablaré | beberé | viviré |
| Tú | hablarás | beberás | vivirás |
| Él, Ella, Elle, Ustedes | hablará | beberá | vivirá |
| Nosotros, Nosotras, Nosotres | hablaremos | beberemos | viviremos |
| Ellos, Ellas, Elles, Ustedes | hablarán | beberán | vivirán |
Recuerda que esta guía esta esta hecha solo para poder crear oraciones básica con una buena sintaxis y así puedas comunicarte.



